Fixxx
Moder
- Joined
- 20.08.24
- Messages
- 1,041
- Reaction score
- 4,023
- Points
- 113

Stealers: One of the Most Common and Deceptive Types of Viruses. They can deceive antivirus software, escape sandboxes and self-delete from the victim's device. Moreover, a malicious actor wishing to steal information doesn't need to be a genius hacker; it's sufficient to simply rent a stealer and use it for their purposes. In this article, we will discuss how stealers work, their characteristics and ways to protect against them.
How Stealers Work
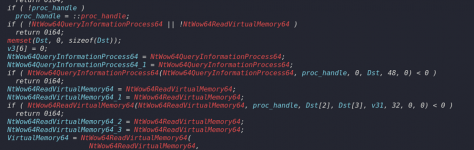
Stealers steal usernames, passwords and other information from the victim and then send this data to the attacker over the internet. The first stealers were quite primitive and designed to steal passwords and other personal information stored in browsers. Over time, they have evolved, becoming more complex and dangerous. It's important to remember that stealers attack not only stationary PCs but also phones, tablets, smartwatches and smart home systems - any device that can collect, process and store data will always be of interest to attackers. Modern stealers can steal data not only from browsers but also from other applications, including messengers, social networks and payment systems. For example, the stealer "(s)AINT" takes screenshots, records all information entered via the keyboard and even uses the webcam to take photos. The virus Mystic Stealer, discovered in 2023, steals user data from crypto wallets and applications. Mystic Stealer can steal data from 40 browsers, including popular ones like Chrome, Edge, Firefox and Opera. It's difficult to say that they have undergone significant changes. Rather, their numbers have increased significantly - especially in open sources like GitHub.
How Stealers Infect Devices
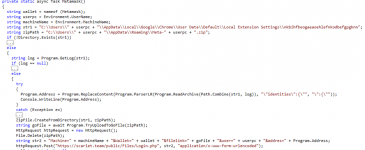
Stealers can enter a user's device in various ways: by visiting infected websites, opening malicious files from emails, etc. For example, attackers disguised the RedLine Stealer virus as a Windows 11 update. They created a Microsoft look-alike site at the domain windows-upgraded.com, from which they distributed malware disguised as an installer. There are many methods of "delivery" for stealers; here are a few:
- Distribution through various forums and blogs, such as cryptocurrency mining or gaming forums. The attacker posts a download link for special software (in the case of cryptocurrency forums) or disguises it as mods (in the case of gaming forums).
- Posting links on video hosting sites. Here, there are several options: the cybercriminal uploads a video to their channel and attaches a malicious link in the comments or posts a link in the comments of someone else's video.
- Phishing on social networks and via email. This spreads similarly to forums. The scammer looks for posts with giveaways, copies the administrator's account and then sends messages to group users with information about winning, which contains malware in the form of a link or attachment.
- Exploit usage. The goal of a cyberattack may be to gain control over the system to elevate privileges or conduct a DoS attack to disrupt system functionality.
- Installation of illegitimate programs. Hackers disguise programs that include malware as legitimate ones. The user downloads and installs the program and along with it, the stealer is installed.
- Injection of web scripts on websites and in advertisements. When a user visits an infected site or sees an infected ad, the stealer can download and install itself on the device.
- Infection via removable media. This was previously a more popular form of malware distribution. Users utilize unverified infected USB drives, SD cards and other removable devices.
Threats and Consequences of Stealers
Some stealers may not activate immediately and have a self-deletion function to make their presence harder to detect. In such cases, the user may not even realize that their data has been stolen and may not take any action. The danger of stealers also lies in the fact that modern viruses have learned to bypass antivirus programs and solutions, such as EDR. Over time, stealers have begun to use more sophisticated masking methods, such as polymorphism and crypters, allowing them to evade antivirus systems. They can now steal not only passwords and files, but also banking data, cryptocurrency and other valuable information. Delivery methods include personalized phishing attacks and advanced social engineering techniques. Modern stealers are often part of multifunctional malware packages that include ransomware, cryptocurrency miners and remote access tools. Attackers use cryptocurrencies to collect ransoms, making them harder to trace.
Currently, attackers don't necessarily have to create their own stealers. Some can be purchased in the dark web as Malware as a Service and obtained via subscription. The information collected by stealers can be used by attackers to extort money, inflict reputational damage on companies or sell the data to third parties. The main distinguishing feature of stealers is the constantly growing number of user programs from which they can steal various information, primarily authentication data. If a program gains noticeable popularity in a certain region, stealer developers adapt their software to maintain the ability to steal data stored within it. This is due to the high competition in the stealer development market. According to information published by researchers at F.A.C.C.T, popular stealers among Russian-speaking cybercriminals, such as RedLine and Racoon, collect the following data:
- Username
- Device name
- Hardware details
- List of installed software
- Saved passwords, cookies, banking card data and cryptocurrency wallet information from browsers.
- Collection of autofill data, cookies and credit card information
- Collection of browsing history and downloaded web pages
- Interception of message history from Telegram
- Theft of cryptocurrency wallet addresses
- Theft of files of specific formats
- Taking screenshots.
Methods of Protection Against Stealers
To protect against stealers, it is essential to follow basic cybersecurity rules. Here are several recommendations:
- Don't open suspicious files in emails, messengers.
- Regularly update software and antivirus programs.
- Use complex passwords that are unique for each service.
- Don't enter confidential information on sites you don't trust.
- Avoid clicking on dubious links and visiting unreliable websites.
- Don't download programs and applications from unverified sources.
Last edited: