Dep
Essential
- Joined
- 15.09.20
- Messages
- 69
- Reaction score
- 296
- Points
- 53
This tutorial in the category WordPress hacking will teach you how to scan WordPress websites for vulnerabilities, enumerate WordPress users accounts and brute force passwords. Enumerating WordPress hackers is the first step in a brute force attack in order to gain access to a WordPress account.
WPScan has the option scan a target website to retrieve a list of account names. IN this tutorial we will also look at How to hide usernames from WPScan so you can avoid the enumeration of user accounts and limit the effectiveness of brute force attempts. We will conclude this tutorial with a demonstration on how to brute force root passwords using WPScan on Kali Linux. WPScan is an auto black box WordPress vulnerability scanner. This tool is a must have for any WordPress developer to scan for vulnerabilities and solve issues before they get exploited by hackers. Together with Nikto, a great webserver assessment tools, this tool should be part of any penetration test targeting a WordPress website or blog.
WPScan comes pre-installed on the following Linux distributions:
The latest version is WPScan 2.8 and the database currently contains:
WPScan update
Start with the following command to update the WPScan vulnerabilities database:
wpscan –update
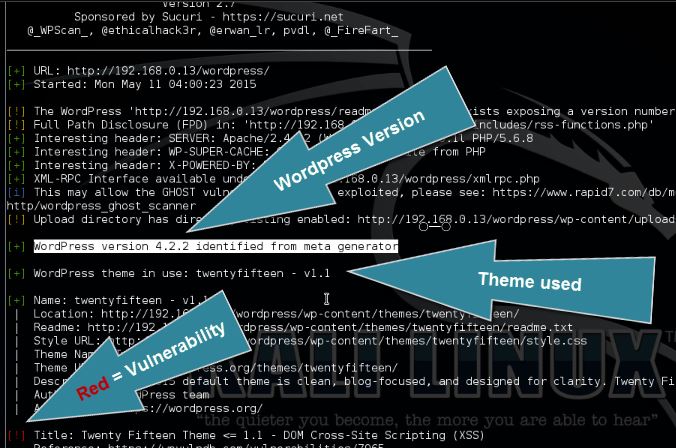
Scanning WordPress vulnerabilities
After updating the vulnerability database use the following command to scan the target website for the most popular and recent vulnerabilities:
wpscan –url [wordpress url]
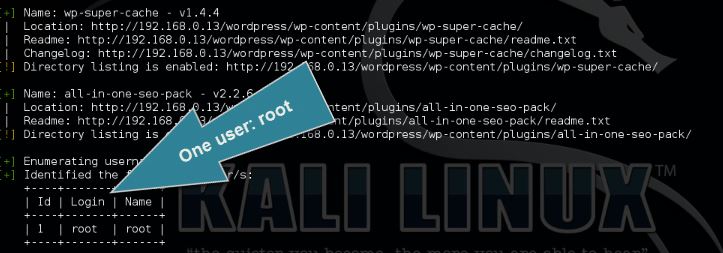
How to enumerate WordPress users
The WordPress user enumeration tool is used the retrieve a list of registered WordPress users for the target host. User enumeration is the first step when an attacker wants to gain access to a specific target by brute forcing. The enumeration tool scans the target on posts, pages and custom types for authors and usernames.
Use the following command to enumerate the WordPress users:
wpscan –url [wordpress url]–enumerate u
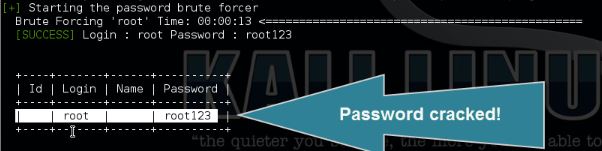
How to brute force the root password
Use the following command to brute force the password for user root:
wpscan –url [wordpress url]–wordlist [path to wordlist]–username [username to brute force]–threads [number of threads to use]
How to avoid WordPress User Enumeration
If you want to avoid WordPress user enumeration, you should avoid using the username as nickname and display name which is shown publicly in WordPress. The best option is to choose an administrator username which consists of random characters and use a different nickname. WPScan scans for usernames in the URL’s so if you won’t use the username it cannot be scanned by WPScan. Another way to prevent user enumeration is to use a different account to publish posts and answer to replies.
How to avoid Wordpress password brute forcing
The best way to keep attack using brute force methods out is to limit the login attempts for and IP address. There are several plug-ins available for WordPress to limit the number login attempts for a specific username and IP, such as Wordfence. The latest WordPress versions have the option to limit login attempts by default. Make sure you limit entries to a maximum of 3 and increase lock out time a lot after 2 lock outs (which is 5 password attempts).
WPScan has the option scan a target website to retrieve a list of account names. IN this tutorial we will also look at How to hide usernames from WPScan so you can avoid the enumeration of user accounts and limit the effectiveness of brute force attempts. We will conclude this tutorial with a demonstration on how to brute force root passwords using WPScan on Kali Linux. WPScan is an auto black box WordPress vulnerability scanner. This tool is a must have for any WordPress developer to scan for vulnerabilities and solve issues before they get exploited by hackers. Together with Nikto, a great webserver assessment tools, this tool should be part of any penetration test targeting a WordPress website or blog.
WPScan comes pre-installed on the following Linux distributions:
The latest version is WPScan 2.8 and the database currently contains:
- Total vulnerable versions: 98
- Total vulnerable plugins: 1.076
- Total vulnerable themes: 361
- Total version vulnerabilities: 1.104
- Total plugin vulnerabilities: 1.763
- Total theme vulnerabilities: 443
WPScan update
Start with the following command to update the WPScan vulnerabilities database:
wpscan –update
Scanning WordPress vulnerabilities
After updating the vulnerability database use the following command to scan the target website for the most popular and recent vulnerabilities:
wpscan –url [wordpress url]

How to enumerate WordPress users
The WordPress user enumeration tool is used the retrieve a list of registered WordPress users for the target host. User enumeration is the first step when an attacker wants to gain access to a specific target by brute forcing. The enumeration tool scans the target on posts, pages and custom types for authors and usernames.
Use the following command to enumerate the WordPress users:
wpscan –url [wordpress url]–enumerate u

How to brute force the root password
Use the following command to brute force the password for user root:
wpscan –url [wordpress url]–wordlist [path to wordlist]–username [username to brute force]–threads [number of threads to use]

How to avoid WordPress User Enumeration
If you want to avoid WordPress user enumeration, you should avoid using the username as nickname and display name which is shown publicly in WordPress. The best option is to choose an administrator username which consists of random characters and use a different nickname. WPScan scans for usernames in the URL’s so if you won’t use the username it cannot be scanned by WPScan. Another way to prevent user enumeration is to use a different account to publish posts and answer to replies.
How to avoid Wordpress password brute forcing
The best way to keep attack using brute force methods out is to limit the login attempts for and IP address. There are several plug-ins available for WordPress to limit the number login attempts for a specific username and IP, such as Wordfence. The latest WordPress versions have the option to limit login attempts by default. Make sure you limit entries to a maximum of 3 and increase lock out time a lot after 2 lock outs (which is 5 password attempts).


